Engine remanufacturing has become one of the most critical pillars of today’s circular economy. As the world faces increasing pressure from resource scarcity, carbon-reduction targets, and rising vehicle ownership, the question becomes unavoidable: how can we give “old engines” a new life without compromising performance or safety? This article takes readers through the evolution of engine remanufacturing from the early days of industrial repair to its modern position as a strategic sustainability solution while highlighting the economic, technical, and environmental benefits that make it indispensable today.
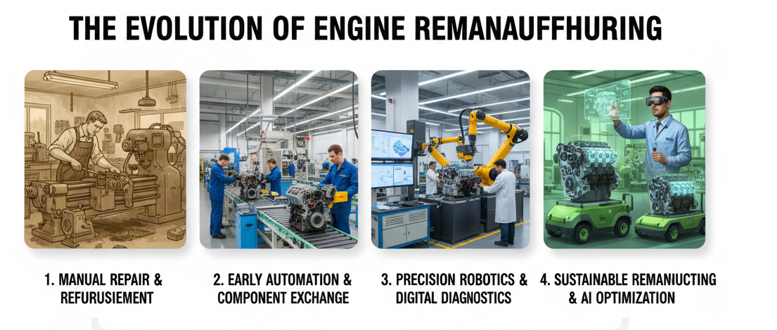
Early Stage: Emergency-Driven Industrial Repair (Late 18th – Mid-20th Century)
The origins of engine remanufacturing can be traced back to the Industrial Revolution, when steam engines and early internal-combustion engines powered factories, ships, and mining operations. At that time, machines frequently broke down due to low machining accuracy and inconsistent materials. Repair work was informal and mostly reactive, which performed by experienced craftsmen whose goal was simply to make the machine run again.
There were no standardized processes, no precision inspection methods, and no concept of rebuilding an engine to “like-new” condition. Repairs rarely restored full performance, and engines often suffered shortened service life. Still, this era laid the foundation for future remanufacturing by proving one simple truth: restoring mechanical components could extend industrial productivity significantly.
Transition Stage: Standardization and Scalable Remanufacturing (Mid-20th Century – 2000s)
The explosion of the automotive industry in the mid-20th century changed everything. Vehicle ownership skyrocketed, and so did the demand for affordable engine replacement options. Purchasing a brand-new engine was often too expensive, which pushed workshops to explore more systematic ways to restore used engines.
This period marked the first major turning point:
- Precision machining tools became widespread, allowing consistent tolerances.
- Diagnostic technologies improved, making defect identification more accurate.
- Trade associations and industry standards emerged, helping define what a “remanufactured engine” should achieve.
Crucially, the mindset shifted from simple repair to true remanufacturing. Engines were now expected to meet performance standards “equal to or better than new,” supported by documented processes and quality benchmarks.
Modern Stage: The Circular Economy Redefines the Industry (2000s – Today)
In the 21st century, engine remanufacturing has fully transformed into a technology-driven, sustainability-aligned, and globally recognized industry.
1. Sustainability Becomes the Core Driver
Governments worldwide promote circular economy strategies, recognizing that remanufacturing is one of the most effective ways to reduce carbon emissions. Studies show that remanufacturing an engine can reduce CO₂ emissions by up to 80% compared to manufacturing a new engine.
2. Advanced Technologies Transform the Process
Modern remanufacturing integrates technologies that were unimaginable in earlier periods:
- AI-powered visual inspection detects micro-cracks and surface defects with exceptional accuracy.
- Laser cladding, 3D printing, and precision machining restore components to like-new specifications.
- Digital traceability systems track every component from core collection to final assembly.
3. Triple Value Creation
Modern engine remanufacturing offers unique value for every stakeholder:
- For enterprises: reduced material costs, improved margins, and new service-based business models.
- For consumers: high-performance engines at significantly lower cost, backed by warranties.
- For society: reduced waste, lower carbon emissions, and increased resource efficiency.
Case Studies: Modern Remanufacturing Success
Industry leaders like Caterpillar and Cummins demonstrate how remanufacturing can become a global, profitable, environmentally aligned business segment.
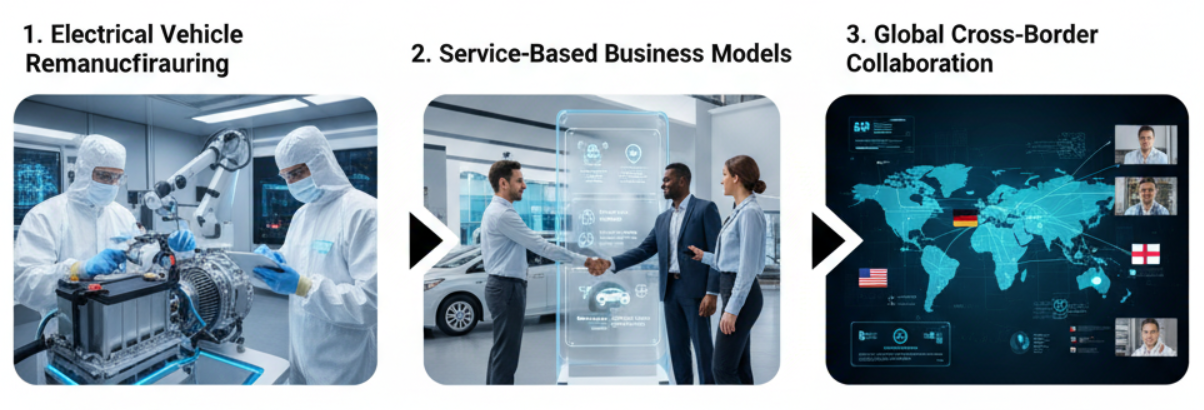
The Future: A New Era of Hybrid, Electric, and Circular Solutions
The next decade will redefine remanufacturing once again:
1. Electrical vehicle powertrain remanufacturing
2. Service-based business models
3. Global cross-border collaboration
Choosing Remanufacturing Means Choosing a Sustainable Future
The journey of engine remanufacturing reflects a powerful evolution of technology, awareness, and responsibility. Engine remanufacturing is no longer an optional solution—it is a cornerstone of a sustainable industrial future.



